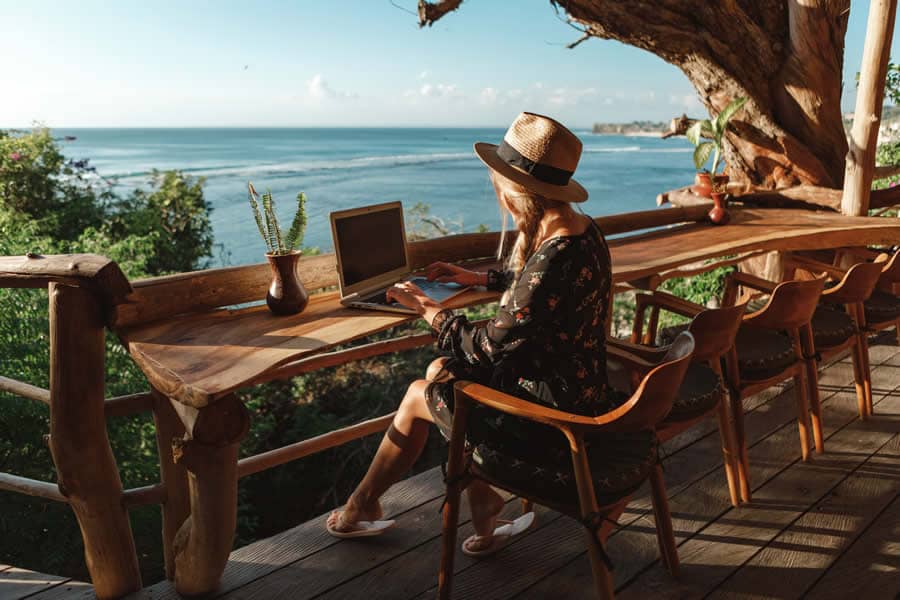
Navigating the complexities of digital nomad taxes can be daunting. It’s crucial, yet often overlooked, to understand the intricacies of tax obligations that come with this fantastic lifestyle. Understanding your tax responsibilities is an essential topic for anyone working remotely. From picturesque locales, whether freelancing from a sunny beach in Bali or developing software in a quaint café in Europe. Our guide aims to simplify the concept of digital nomad taxes, ensuring you’re well-informed about your tax duties. We will also cover the best tax havens and the best countries for digital nomad tax along with some of the more advanced strategies to ensure you pay less tax while still being compliant.
This approach to understanding digital nomad taxes will highlight how to navigate various tax jurisdictions and optimize your tax situation. Knowing how to handle your taxes efficiently can prevent them from becoming an obstacle in your nomadic journey. With our guidance, you can learn the essential strategies for managing your taxes as a digital nomad. This includes establishing your tax residency to leveraging work-related expenses. We aim to demystify the tax process, offering practical advice to ensure you can focus more on your passions and less on paperwork. By addressing the critical aspects of digital nomad taxes, we’re here to help you manage your taxes effectively. We know this will allow you to enjoy the nomadic lifestyle without tax-related worries.
What Does The Average Digital Nomad Earn?
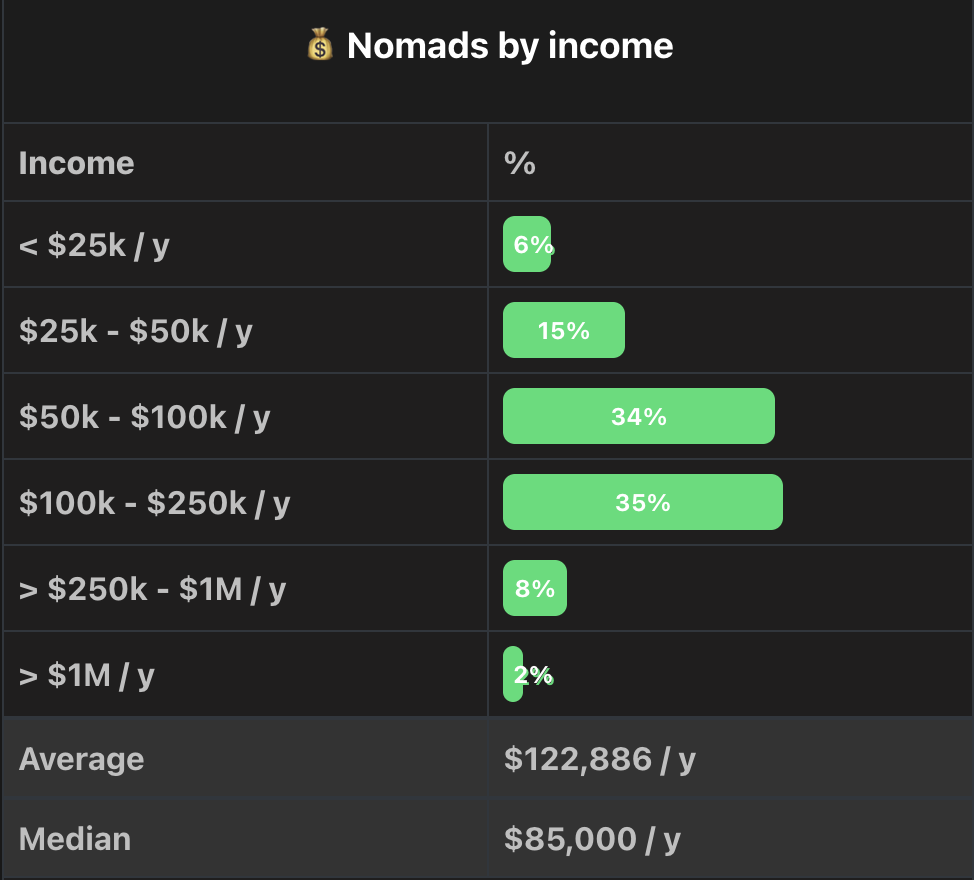
Some people don’t realize this, but digital nomads are some of the highest-income earning cohorts in the world. But, most don’t have a good handle on their tax situation and think that because they are not a tax resident anywhere, they are not obligated to pay taxes. 99% of the time, this is not true! But, the reality is that the governments are only going to come after you if your income or wealth is over a certain threshold. None of this matters if you are planning on staying broke the rest of your life and having no assets.
While there’s potential for a lucrative digital nomad career, it’s not without its financial management challenges. It’s also noteworthy that the quest for a digital nomad tax free status might be enticing but requires understanding of the laws and regulations of respective jurisdictions. This is where understanding your average earnings becomes crucial. Knowing what you’re likely to earn helps in forecasting your tax liabilities, ensuring you don’t get caught off-guard when tax season approaches.
Throughout research, we have seen that being a digital nomad entails not just embracing the freedom of location but also the responsibility of managing one’s finances and taxes. The dream of travelling the world while working remotely doesn’t exempt one from the due diligence required in tax planning. The key lies in finding the balance between optimizing your earnings and complying with tax obligations, wherever you might be.
Understanding Digital Nomad Taxes

Navigating the complexities of taxes as a digital nomad can initially seem daunting. However, with some insight and preparation, it’s entirely manageable. In this section, we will delve into what exactly being a digital nomad entails and how taxes work for individuals embracing this lifestyle.
What is a Digital Nomad?
A digital nomad leverages technology to work remotely, often travelling to different countries while maintaining professional responsibilities. This lifestyle offers unparalleled flexibility and freedom, enabling individuals to explore new cultures and experiences without being tied to a single location. Despite the allure of living a digital nomad tax free life, it’s crucial to understand that tax obligations do not simply vanish when you start living out of a suitcase. Therefore, staying informed and compliant with tax laws in various jurisdictions becomes a part of the nomadic journey.
How Taxes Work for Digital Nomads
Navigating taxes as a digital nomad involves understanding international tax laws. Due to the absence of a fixed residence, this often makes tax compliance more complex. Generally, digital nomads are taxed on worldwide income by their country of citizenship or where they’re considered tax residents. However, frequently moving means they often don’t meet residency requirements in any one country, creating a need to understand “tax home,” “tax residency,” and international tax treaties to avoid double taxation. While the idea of living tax-free is mostly a myth, strategic tax planning and knowledge of tax implications in various destinations are key to managing liabilities.
Countries like the United Arab Emirates, Malaysia, and Antigua and Barbuda have introduced policies and special visas with tax incentives for digital nomads. These countries recognize their contribution to the economy and creating attractive tax havens for digital nomads. These initiatives simplify tax situations for nomads and reflect a growing trend of nations adapting to the digital nomad lifestyle. By selecting destinations with favorable tax treatments, digital nomads can optimize their tax positions, ensuring their lifestyle is both enjoyable and financially sustainable.
Maintaining a balance between the digital nomad lifestyle and tax obligations is essential for long-term sustainability. It’s about avoiding penalties and ensuring the lifestyle is viable over time. Utilizing tax consultants knowledgeable in nomadic taxes or software for tracking international tax obligations can be crucial. Investing in financial literacy and tax planning is as important as selecting the right travel gear. Ideally as a digital nomad you want to roam freely without the burden of tax complications.
Tax Considerations for Digital Nomads

As we navigate the intricacies of living the digital nomad lifestyle, we have come to realise the paramount importance of understanding the tax implications that accompany this choice. It’s about the freedom to work from anywhere and knowing how to manage your taxes efficiently. Below, I’ll break down some of the key tax considerations essential for every digital nomad to grasp.
Tax Residency for Digital Nomads
One of the first things to learn on your journey is the concept of tax residency and understanding what countries you have tax obligations in. Your tax residency determines which country has the right to tax your income. This can become complicated for digital nomads due to the lack of a permanent residence. Many countries use the 183-day rule—if you spend more than half the year (183 days) in a single country, you could be considered a tax resident there. However, some nations have low minimum-stay requirements and are considered tax havens for digital nomads. Make sure you research and understand the rules specific to the countries you spend time in. The key to managing your tax residency is careful planning and documentation of your whereabouts.
Establishing a Tax Home
The idea of a tax home is somewhat elusive for digital nomads. In general, your tax home is the place where you primarily conduct your business. However, establishing a tax home can be challenging for those of us constantly on the move. Why is this important? Having a defined tax home can impact your tax obligations significantly. For example, establishing a foreign tax home as a US citizen can qualify you for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion. This has the potential to allow you to exclude a portion of your income from US taxes. To establish a tax home, you must prove that your business activities are centred outside the US and you have significant ties to a location. But this is often not the case for digital nomads travelling perpetually.
Tax Treaties and Exclusions
Another critical aspect most encountered is the role of tax treaties and exclusions. Many countries have tax treaties with one another to avoid double taxation of the same income. As a digital nomad, being aware of these treaties and agreements is essential to leverage any benefits. You want to avoid paying more tax than necessary. Moreover, some countries offer special tax exclusions or incentives for digital nomads. However, I’ve learned that living completely digital nomad tax free is more of a myth than reality. It’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional who can provide advice tailored to your situation.
Deductible Expenses for Digital Nomads
One benefit of running your business from different parts of the world is the potential to deduct certain expenses. As I manage my finances, I’ve identified various deductible expenses that directly relate to my nomadic lifestyle, such as:
- Travel Costs: Flights, accommodation, and local transportation can sometimes be deducted if they’re necessary for your business.
- Workspace: Membership fees for coworking spaces could be considered necessary business expenses.
- Technology Subscriptions: Expenses for software or services necessary for communication and managing your business can also be deductible.
It’s important to keep thorough records of these expenses and understand the tax rules in your home country regarding deductions. These deductions can significantly reduce your taxable income, but they require diligent record-keeping and sometimes the guidance of a tax professional.
The Best Digital Nomad Tax Free Countries

When I’m exploring options for my digital nomad lifestyle, I’m particularly drawn to countries that not only embrace the digital nomad culture but also offer attractive tax benefits. Through my experiences and research, I’ve found that certain destinations stand out regarding tax incentives for digital nomads. Here, I’ll share insights into some of the best digital nomad tax-free countries that have caught my attention.
Dubai (UAE)
The United Arab Emirates, particularly Dubai, has fast become a hotspot for digital nomads. Not only does its vibrant city life and high-speed internet appeal to those who work online, but it also offers significant tax advantages. The UAE does not levy personal income tax and has several tax-free company formation options. This makes it an ideal destination as a tax haven for digital nomads looking to maximize their earnings. Additionally, with the introduction of digital nomad visas, Dubai is inviting digital nomads to take advantage of its tax-free living.
Thailand
Thailand is another country on the radar for many digital nomads, particularly its affordability and beautiful landscapes. While not entirely tax-free, Thailand offers a beneficial tax regime for foreign earners. If you live in Thailand and are considered a tax resident, foreign-earned income is not subject to tax. The caveat is that it’s not brought into the country within the same year it’s earned. They made significant changes to this program and are now much more strict. But, this territorial tax set up still makes Thailand an attractive destination for digital nomads looking to balance work and paradise.
Malaysia
Malaysia’s Malaysia My Second Home (MM2H) programme is an initiative to make Malaysia a top destination for digital nomads. It’s one of the most affordable developed countries in the world and in a ideal location for perpetual travel. Under this program, individuals who meet certain criteria can receive a long-term visa and tax exemptions on foreign-earned income. There is some complexity involved in structuring, but it is a relatively low cost option as a tax haven for digital nomads. This makes Malaysia a culturally rich and diverse destination and a financially strategic choice for digital nomads.
Costa Rica
Costa Rica offers a Nomad Visa, specifically designed for individuals who can prove a stable foreign income. Most digital nomads can meet these income requirements. This Central American country has a territorial taxation system, meaning it does not tax foreign-earned income. With the right structuring, digital nomads can enjoy a high standard of living without worrying about a large tax bill. Costa Rica’s focus on sustainability makes it an ideal destination for those looking to work in a peaceful and inspiring environment.
Antigua and Barbuda
The Digital Nomad Visa by Antigua offers digital nomads the chance to live and work in this Caribbean haven. It’s a two year program, however, it’s key to note that under this program, participants won’t be considered tax residents. This is often misunderstood and may pose tax implications for those with ties to countries like Canada or the UK. Yet, for digital nomads able to disconnect from their home countries’ tax systems, this initiative presents an attractive option for blending remote work with island living.
Moreover, Antigua and Barbuda is becoming a favored destination for its safety and quality of life. This is especially among affluent families in their 30s and 40s with young children looking for a low tax home. The islands’ safety, vibrant culture, and relaxed lifestyle make them a prime relocation choice. The Nomad Digital Visa Program adds to the interest, offering families and professionals a unique opportunity to experience the Caribbean lifestyle. This balance of work, life, and safety is making Antigua and Barbuda an increasingly popular choice for those seeking an idyllic yet productive life.
Panama
Panama’s Friendly Nations Visa is designed to attract foreigners, including digital nomads, by offering them a path to residency. One of the compelling benefits of living in Panama as a digital nomad is the territorial tax system, meaning only income earned within the country is taxed. Therefore, foreign income, such as earnings from remote work for non-Panamanian companies, remains tax-free. Panama combines the allure of tropical beauty with substantial financial benefits, making it a lucrative option for digital nomads.
In navigating your journey as a digital nomad, it’s important to have an understanding the tax implications in each country. These destinations offer breathtaking landscapes, rich cultural experiences and practical benefits that can significantly impact a digital nomad’s financial well-being.
Managing Digital Nomad Finances

Navigating the financial landscape as a digital nomad presents unique challenges, especially when it comes to taxes. A well-structured approach to finance management can make the difference between thriving and surviving in this lifestyle.
Keeping Track of Income and Expenses
The cornerstone of solid financial management as a digital nomad is meticulous record-keeping. Understanding the flow of income and outgoings is crucial. Using digital tools and apps for budgeting and tracking expenses simplifies this process enormously. It’s also essential for preparing for tax season, as it helps identify deductions and ensure you are not overpaying on taxes. To make the most of low tax opportunities, you should keep detailed records of work locations, durations, and income sources. This will prove invaluable for determining your tax obligations across different jurisdictions.
Setting Up a Digital Nomad Business
Many digital nomads opt to formalize their work into a business structure. Setting up a business entity, such as a Limited Liability Company (LLC), can provide significant tax advantages and give a clear framework for managing my finances. By choosing the right business structure, you can optimize for tax benefits, specifically in digital nomad friendly countries. It’s a strategy that requires careful planning but can significantly reduce my tax liabilities while ensuring I comply with local laws.
Working with an Accountant or Tax Professional
Given the complexity of tax laws across different countries, working with an accountant or tax professional is invaluable. Ideally, these people are well-versed in international taxation and, specifically, the nuances of digital nomad taxes. This partnership has been critical in navigating double taxation treaties, and the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) for US-citizens. A qualified professional helps me remain compliant with tax laws wherever you are while ensuring you are not leaving money on the table. Moreover, they can offer guidance on structuring business and income to take full advantage of individual countries incentives.
Tips for Minimizing Tax Liabilities

In my journey as a digital nomad starting in my 20’s, I’ve realised the importance of effectively managing tax liabilities. It’s not just about compliance but also smart financial planning to ensure that I’m not overpaying in taxes. Here, I’ll share some strategies I’ve found instrumental in reducing my tax burden.
Utilizing Tax Deductions and Credits
One of the first areas I explored to minimize my tax liabilities was through deductions and credits. It’s crucial to understand the difference between the two. Tax deductions reduce the income subject to tax, while tax credits reduce the tax owed, dollar for dollar. As a digital nomad, several deductions and credits can be particularly beneficial.
- Home office expenses: Working remotely often means that most of my living space is dedicated to work. This enables me to deduct expenses related to this space, such as a percentage of rent, utilities, and internet service.
- Travel expenses: Traveling to and from client meetings or conferences can add up. I ensure to track these expenses as they are often deductible.
- Education and training: Keeping my skills sharp is key to remaining competitive. Courses and professional development related to my trade or business are generally deductible.
Being diligent about recording these expenses has significantly lowered my taxable income, naturally leading to reduced tax liabilities.
Taking Advantage of Tax-Free Retirement Accounts
Another strategy I’ve employed is contributing to tax-free retirement accounts. Many countries offer retirement accounts that enjoy tax-free growth, allowing contributions to grow tax-free until retirement. As a digital nomad, navigating these accounts can be complex due to varying country laws. However, finding a suitable scheme and making regular contributions has been a game-changer.
In Canada, for instance, the Self-Directed RRSP is beneficial as it allows for tax-free growth and withdrawals. There is also a first-time home buyers program that can be utilized to purchase your first home or investment property. This means I can invest a portion of my earnings and not worry about the tax implications of the growth of these investments.
Utilizing Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
Lastly, tax-efficient investment strategies have significantly influenced my financial planning. This involves choosing investments that are taxed at a lower rate or not at all. For example, long-term capital gains are often taxed at a lower rate than short-term gains.
In addition, investing in tax-advantaged accounts or products specific to digital nomads can be highly effective. For instance, some countries offer digital nomad tax-free incentives, such as reduced tax rates on foreign-sourced income, which can make certain investments more attractive.
Navigating tax liabilities as a digital nomad involves a combination of compliance and strategic financial planning. By utilizing tax deductions and credits and employing tax-efficient investment strategies, you can reduce your tax burden while adhering to the laws of my jurisdictions. Remember, it’s always wise to consult with a tax professional well-versed in the complexities of digital nomad taxes to tailor these strategies to your specific situation.
Filing Taxes as a Digital Nomad (US Citizens)

Navigating the maze of taxation laws can be daunting for anyone. And when you’re a digital nomad, the complexity seems to magnify. With a lifestyle that transcends borders, understanding how to file taxes correctly ensures that you remain compliant.
Self-Employment Taxes
As a digital nomad, most of my income often falls under self-employment. This categorization carries with it specific tax implications, particularly concerning Self-Employment Taxes. These taxes cover Social Security and Medicare contributions, normally covered by an employer.
For digital nomads based in the U.S. or those earning from U.S. sources, the self-employment tax rate is 15.3%, divided as 12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare. It’s crucial to factor these percentages into financial planning to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
Furthermore, certain deductions relevant to self-employment can reduce taxable income. Expenses like business-related travel, workspace costs, and even health insurance premiums may qualify. Maintaining meticulous records of these expenses is vital to leverage potential tax benefits fully.
Reporting Foreign Income
The ability to work from any corner of the globe presents unique tax considerations. For British digital nomads, like myself, reporting foreign income becomes a pivotal aspect of tax compliance. The cornerstone of this process is understanding residency and domicile statuses as they significantly influence tax liabilities.
For instance, if I’m a resident in the UK but work in another country, I must report worldwide income to HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC). This income is potentially subject to double taxation. However, the UK has double taxation agreements with numerous countries, which can alleviate this issue.
Digital nomads should be aware that many nations require reporting of global income if they’re deemed tax residents, typically determined by the number of days spent in the country. This underscores the importance of aligning one’s lifestyle with the most favourable tax jurisdictions.
Choosing the Right Tax Form
Determining which tax form to file depends largely on one’s residency status and the specifics of their global income. For digital nomads from the U.S., forms extend beyond the standard 1040 to include forms like the 2555, which relates to Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE), and the 1116, for Foreign Tax Credit (FTC).
Both the FEIE and FTC are instruments designed to mitigate the potential of double taxation by excluding a portion of foreign income from U.S. taxes. It also credits taxes paid to other countries. Navigating these options mandates an understanding of tax laws. It also often requires consultation with a tax professional to ensure optimal filing.
Identifying the most beneficial tax form and leveraging international tax treaties can significantly impact the financial outlook of a digital nomad. Armed with this knowledge, I’m better positioned to make informed decisions that promote tax efficiency and legal compliance.
Conclusion

Navigating the tax landscape as a digital nomad can seem daunting at first. Yet, managing your finances effectively while roaming the globe is possible with the right strategies and guidance. I’ve delved into various methods to minimize tax liabilities, from leveraging tax deductions to investing wisely. Remember, the key lies in understanding your tax obligations and planning accordingly. Dan Merriam and Offshore Freedom is an expert in this field, offering unfiltered advice to enhance your financial freedom significantly. Embracing his expertise could be your first step towards a more secure and prosperous nomadic lifestyle. Taking control of your taxes is not just about compliance. It’s about unlocking a world of opportunities for growth and adventure.
Learn More
Offshore Freedom™ is a boutique coaching and consulting firm that helps investors and entrepreneurs live and invest internationally. We help our clients grow their businesses, pay less taxes, buy more real estate, and take advantage of global residency and citizenship by investment programs worldwide.
Schedule a 1 on 1 consultation with Dan Merriam, and let us help you design the life of your dreams and live the Offshore Freedom™ lifestyle. Ask questions and get answers about international real estate, tax planning, offshore banking, second residencies, citizenship by investment, lifestyle design and more.
This article is for informational purposes only; it should not be considered financial, tax planning, investment or legal advice. Consult a certified financial or investment professional in your jurisdiction of interest before making any major financial or investment decisions.
Writer in Tax Reduction, International Tax Planning, Travel, Citizenship by Investment, Real Estate Investing, Digital Nomad Taxes, Second Residence, Real Estate Investing, How Digital Nomad Taxes Work, Asset Management, Lifestyle Planning, Countries with the Lowest Taxes, Company Formation, Offshore Banking, Asset Protection, Technology, Entrepreneurship


















